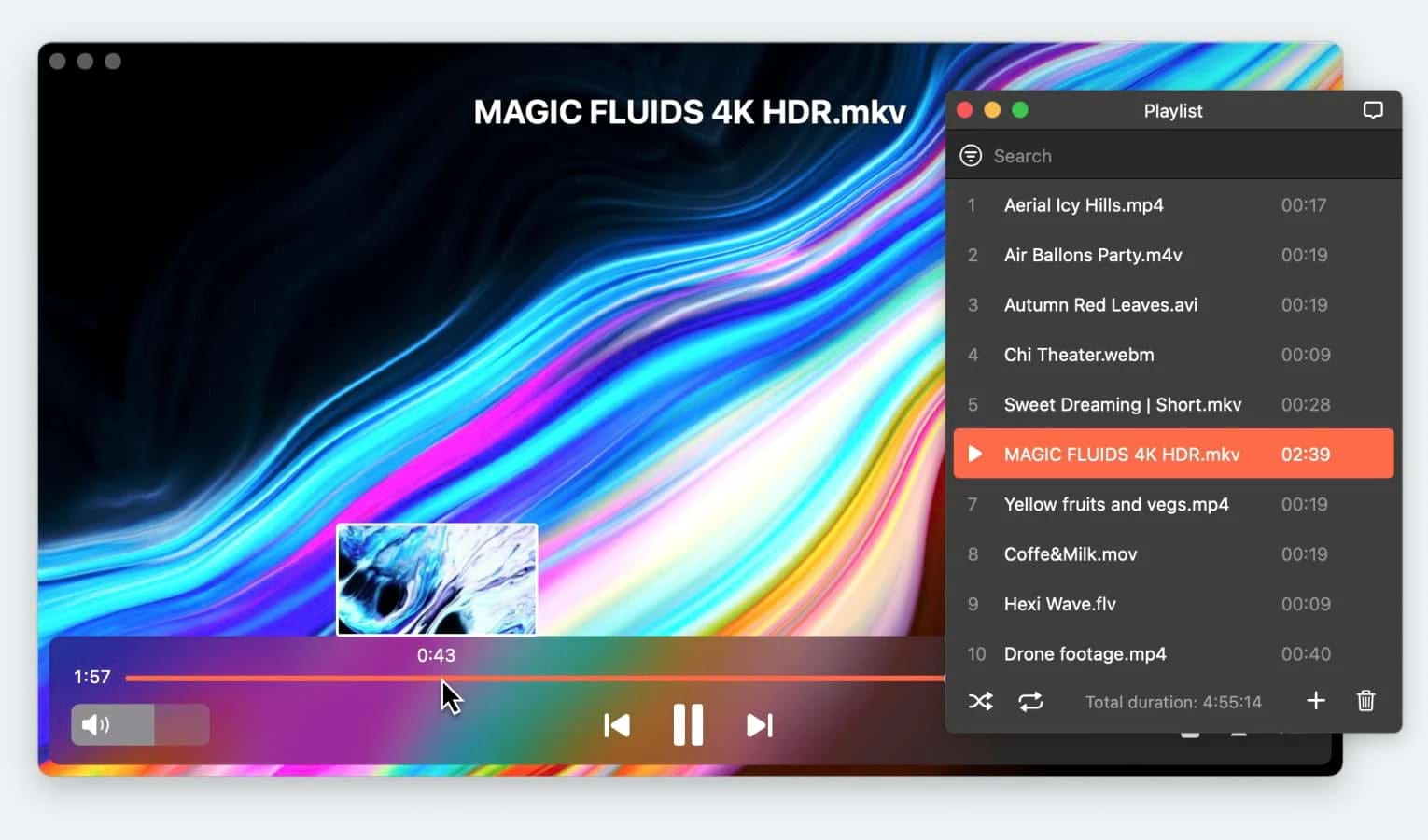
MP4 and MKV are two of the most popular video formats used daily by many, but how many of us actually know the difference between them? Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help you decide which format is best for your needs.
Is MKV or MP4 better? What is .mkv file? These are the sorts of questions we will answer in this article. We’ll break down the differences between these two formats to help you determine the best choice for you.
What is MKV Format
MKV, or Matroska Video, is a video format that’s capable of storing multiple video, audio, and subtitle tracks all in one file. If you frequently watch videos and movies with different languages, then MKV is one of the best formats to use.
What sets MKV file format apart from other formats is its ability to handle almost any video or audio codec, which means you can store high-quality videos without compromising on performance or compatibility. MKV also lets you add features like chapter markers, subtitles, text fields, and even attachments like images or documents.
It’s free, open-source, and supported by a large community that regularly updates it. If you want to have more control over your media files and you like extra features, MKV is a great choice.

What is MP4 File Format
MP4 is one of the most widely used video file formats today. It’s a multimedia container that can store video, audio, subtitles, and images. One of the reasons MP4 is so popular is because of its ability to compress video and audio without losing too much quality. That’s why it’s widely used on the internet, where keeping file sizes smaller is important.
The full name of MP4 is MPEG-4 Part 14, not MPEG-4. MP4 and MPEG-4 are essentially the same thing, but there is a slight technical difference between the two. The former refers to the multimedia container format that stores all the media files. The latter, on the other hand, refers to the multimedia standard that defines how video and audio are compressed and encoded.
MP4 files are supported by virtually all known devices and platforms, including computers, phones, and tablets. The format is also often used for online video streaming because it keeps file sizes smaller while maintaining good video and audio quality.

MP4 and MKV: Key Differences
In this .mkv vs .mp4 comparison section, we’re going to look at some of the main differences between the two formats:
Quality
When it comes to quality, both MKV and MP4 are capable of storing high-definition video.The quality of the video depends on the codec used to compress it, rather than the container format itself.
Fortunately, both formats support a wide variety of video and audio codecs. MP4 commonly uses codecs like H.264 and AAC, while MKV can support a broader range, including H.264, HEVC, VP9, and many others.
Keep in mind that MP4 and MKV are output formats and not encoding formats. This means that the actual video and audio quality will depend entirely on the video and audio codecs used for compression.
File Size
The next characteristic to compare MKV and MP4 is the file size. As with the quality, the size also largely depends on the codecs used instead of the format itself. That’s not to say the format doesn’t play a role; there are some general trends when comparing MKV and MP4.
MKV files are usually bigger because they support extra features like multiple audio tracks, subtitles, and attachments.
MP4 files, on the other hand, are built for better compression, which makes it easier to stream them online. With codecs like H.264 or H.265, MP4 reduces file size without losing much quality. That’s why you’ll almost always see MP4 files used for streaming, social media, and mobile devices.
If you use the same codec and bitrate for both formats, their file sizes will be almost the same. But MKV files will still often be larger because of the added features.
Compatible Audio and Video Codecs
The main difference between MKV and MP4 is that the former is an open-standard container, which means it supports a much wider range of video and audio codecs. Some of the video codecs it works with include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), VP9, and AV1, while audio codecs include MP3, AAC, AC3, DTS, and FLAC.
Being able to support FLAC is a huge advantage because it’s a lossless audio codec, which means it preserves the original quality of the audio without any compression or loss of detail.
MP4 is a bit limited in terms of codec support compared to MKV. While it works well with widely-used codecs like H.264 and H.265 for video, and AAC, MP3, and ALAC for audio, it doesn’t support more advanced or lossless codecs like FLAC.
ALAC is a good alternative to FLAC, but it’s not as efficient, which may make it less appealing to audiophiles who prioritize high-quality, lossless audio.
That being said, MP4 remains the most widely used format on the internet, largely due to its compatibility with most commonly used codecs.
Supported Platforms
Despite the fact that MKV supports more codecs, MP4 is more compatible with a wider range of devices. It works well across phones, tablets, computers, and even game consoles like PlayStation and Xbox.
It’s also supported by popular video editing programs like iMovie and Final Cut Pro, as well as media players like Elmedia Player and Blu-ray players.
MKV has limited compatibility across devices and platforms. Although many media players and software can play MKV files, you might run into compatibility issues, especially with older devices or systems.
Advantages of MKV
Which is better, MKV or MP4? Let’s take a look at the main advantages of each format:
- MKV is an open-source format, which means there are no licensing fees involved in using it. This is its biggest advantage.
- It handles multiple audio tracks, subtitles, and even chapter markers much more effectively than MP4.
- You can use multiple languages for audio tracks and subtitles in an MKV video.
- While resolution depends on the source and codec, MKV files are often used to store high-resolution video due to their flexibility.
- MKV can handle almost any type of video and audio codec.
Advantages of MP4
Here are some advantages of the MP4 format:
- MP4 works across almost every browser, operating system, and device, including phones, tablets, and smart TVs.
- MP4 files are compressed efficiently, making them smaller in size without sacrificing quality. This results in faster downloads and easier storage.
- MP4 is the preferred format for online video streaming.
- When paired with H.264 encoding, MP4 delivers high-quality video with a relatively small file size, making it perfect for both storage and playback.
The Practical Difference Between MKV and MP4
| Use case | Notes on MKV | Notes on MP4 |
| Distribution (paid or free) | Open and free, but might not be supported by some platforms | Use cautiously; beware of patent protection. Likely supported everywhere |
| Sharing | Less compatible overall | Works well with messengers and hosting services |
| Embedding | WebM is more modern, and worth looking into | Technically works, but with issues. Video can not be truly cached, only downloaded in large chunks |
| Streaming | Entirely possible | Possible, with workarounds |
| Preservation | More DVD-like features, broader choice of codecs | Just good enough |
| Editing | May cause issues and waste time in production. Good choice for the final product. Plenty of documentation and community help | Easily and quickly opened in editors |
| Mobile entertainment | Usable, but may cause lag and battery drain | Battery-efficient and fast |
MKV vs MP4: Which Format Is Right for You?
The answer is that it depends on your specific needs. If you want a format that supports multiple audio tracks, subtitles, and high-definition video, MKV is the way to go. It offers more flexibility with codecs and features.
However, if compatibility, ease of use, and file size are your top priorities, MP4 is the better choice.
If you’re on a Mac and need to play MKV files, we recommend checking out Elmedia Player. Elmedia supports all your media without compatibility issues and offers handy features like chapter marking, bookmarking, and importing subtitles in incompatible formats.
FAQ
Because they are only containers, MKV vs MP4 quality wise don’t make a difference. In fact, videos in both formats can have the same encoding, with the same size and the same quality.
If your MKV and MP4 contain the same video, there are two possible reasons: either your MKV file has higher compression, or it uses a different, more efficient codec.
It’s not a simple question, refer to the article above. But if you’re in a rush, an MP4 is easier and faster to encode. Just make sure you don’t monetize it.
If your MKV is encoded with an MPEG codec, you can. For example, VLC gives you the option to “keep video” when converting; this way, it will just transfer the video stream to a new MP4 container without converting it. You can also use Elmedia to play MKV on Mac without conversion.
It’s open and free, it can hold most codecs in existence, and it has some nice DVD-like features.